ViT를 읽고 Pytorch로 구현해보았다. 원본 코드는 jax로 구현되어 있기에 깃허브에서 star가 높은 레포를 참고해 진행하였다.
dropout은 생략하고 구현했으니 주의!
참고한 레포 링크: https://github.com/lucidrains/vit-pytorch
GitHub - lucidrains/vit-pytorch: Implementation of Vision Transformer, a simple way to achieve SOTA in vision classification wit
Implementation of Vision Transformer, a simple way to achieve SOTA in vision classification with only a single transformer encoder, in Pytorch - GitHub - lucidrains/vit-pytorch: Implementation of V...
github.com
Patch embedding
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, batch_size, num_classes, dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim, img_dim = [3,224,224], patch_dim = [3,56,56], dim_head = 64):
super().__init__()
image_h = img_dim[1]
image_w = img_dim[2]
patch_h = patch_dim[1]
patch_w = patch_dim[2]
n_patches = (image_h // patch_h) * (image_w // patch_w)
embedding_dim = img_dim[0] * patch_h * patch_w
self.patch_dim = patch_dim
self.img_dim = img_dim
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.n_patches = n_patches
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
#so we flatten the patches and map to D dimensions with a trainable linear projection (Eq. 1).
self.prejection = nn.Sequential(
nn.LayerNorm(embedding_dim),
nn.Linear(embedding_dim, dim),
nn.LayerNorm(dim)
)
self.pos_embedding =nn.Parameter(torch.randn(n_patches+1, dim))
self.cls_token =nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, dim))
def forward(self, img):
channels=img.shape[1]
x = img.unfold(2, self.patch_dim[1], self.patch_dim[2]).unfold(3, self.patch_dim[1], self.patch_dim[2])
x = x.contiguous().view(self.batch_size, channels, self.n_patches, self.patch_dim[1], self.patch_dim[2])
patches = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 4, 1)
x = patches.contiguous().view(self.batch_size, self.n_patches, self.embedding_dim)
x = self.projection(x)
return x
patch로 만드는 과정은 $H \times W \times C$ 에서 $N \times (P^2 \cdot C)$ 로 차원을 변경해줘야 하며 주로 Unfold나 einops를 사용해 구현된 예제가 많았다. 마지막의 self.projection은 아래 노란줄의 flatten 후 D차원으로 linear projection하는 부분이다.
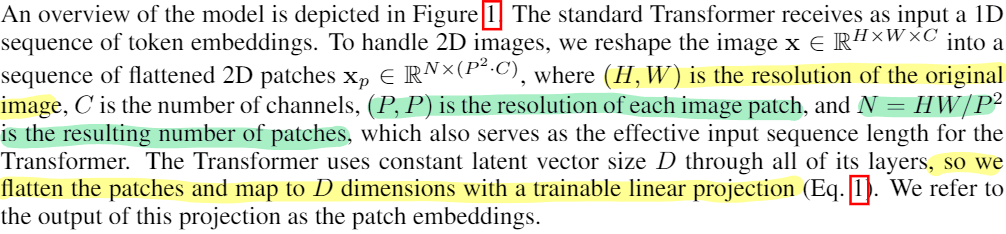
def __init__(self, batch_size, num_classes, dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim, output_dim, img_dim = [3,224,224], patch_dim = [3,56,56], dim_head = 64):
#...
self.cls_token =nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, dim))
self.pos_embedding =nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, n_patches+1, dim))
def forward(self, img):
#...
cls_tokens = self.cls_token.repeat(self.batch_size, 1, 1)
x = torch.cat([cls_tokens, x], dim=1)
x = x + self.pos_embedding[:, :(self.n_patches+1)]
return xembedding은 nn.Parameter를 사용해 구현했다. 코드의 cls_tokens와 self.pos_embedding이 논문의 식에서 $x_{class}$와 $E_{pos}$를 의미한다.
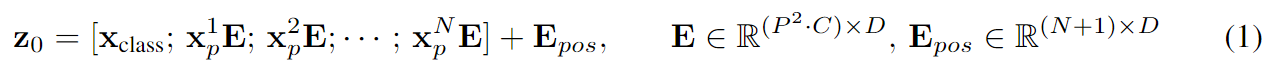
Multi Head Attention
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, heads = 8):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.dim_heads = dim // heads
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.to_qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3)
self.MHA = nn.MultiheadAttention(dim, heads, batch_first=True) #dim means input sequence's dim
def forward(self, x):
x = self.norm(x)
qkv = self.to_qkv(x).chunk(3, dim=-1) #example: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.chunk.html
q, k, v = [token for token in qkv]
result = self.MHA(q,k,v, need_weights=True)[0]
return resultMHA는 pytorch에서 제공하는 Module이 있길래 사용해봤는데 문제 없이 동작했다. q, k, v를 만들고 MHA에 넣어주면 연산을 수행 후 batch_size, seq_len, dim 형태로 return 해준다.
attn = Attention(dim=768, heads=8)
temp_tensor = torch.randn([16, 100, 768])
result = attn(temp_tensor)
print(result.shape)
--------------------------------------------------------
torch.Size([16, 100, 768])
Transformer
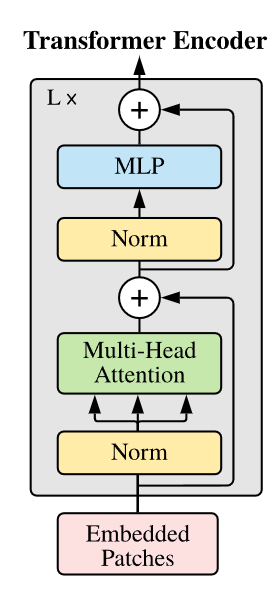
이전에 구현했던 Attention module(초록색)과 layer normalization, MLP를 조합하면 ViT에서 사용하는 Transformer를 구현할 수 있다.
class FeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, mlp_dim):
super().__init__()
layers = []
layers.append(nn.LayerNorm(dim))
layers.append(nn.Linear(dim, mlp_dim))
layers.append(nn.GELU())
layers.append(nn.Linear(mlp_dim, dim))
self.net = nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self,x):
return self.net(x)class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim): #in paper head_dim = dim * 4
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([])
for _ in range(depth):
self.layers.append(nn.ModuleList([(Attention(dim, heads)),(FeedForward(dim, mlp_dim))]))
def forward(self,x):
for attn, ffn in self.layers:
x = attn(x) + x
x = ffn(x) + x
return x논문에서는 FFN의 연산순서를 정확히 기재하지는 않았는데 대다수의 구현체에서 norm->Linear->GELU->Linear를 사용했다. Transformer를 구성하는것은 이전의 모듈들과 residual 연산을 적절히 넣으면 된다.
Classification head
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, batch_size, num_classes, dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim, output_dim, img_dim = [3,224,224], patch_dim = [3,56,56], dim_head = 64):
#...
self.transformer = Transformer(dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.classification_head = nn.Linear(dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, img):
#...
x = self.transformer(x)
x = x[:,0]
x = self.norm(x) #is this order right?
x = self.classification_head(x)
#많은 구현체에서 norm순서나 유무 vatiation이 많았다
return x예상보다 이 부분에서 변형이 많았는데 나는 참고한 레포 그대로 norm 이후 liner을 사용하여 구현했다.
ViT
ViT모듈을 구현한 전체 코드는 아래와 같다.(Transformer, FFN, Attention은 그대로 사용)
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, batch_size, num_classes, dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim, output_dim, img_dim = [3,224,224], patch_dim = [3,56,56], dim_head = 64):
super().__init__()
image_h = img_dim[1]
image_w = img_dim[2]
patch_h = patch_dim[1]
patch_w = patch_dim[2]
n_patches = (image_h // patch_h) * (image_w // patch_w)
embedding_dim = img_dim[0] * patch_h * patch_w
self.patch_dim = patch_dim
self.img_dim = img_dim
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.n_patches = n_patches
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
#so we flatten the patches and map to D dimensions with a trainable linear projection (Eq. 1).
self.projection = nn.Sequential(
nn.LayerNorm(embedding_dim),
nn.Linear(embedding_dim, dim),
nn.LayerNorm(dim)
)
self.cls_token =nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, dim))
self.pos_embedding =nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, n_patches+1, dim))
self.transformer = Transformer(dim, depth, heads, mlp_dim)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.classification_head = nn.Linear(dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, img):
channels=img.shape[1]
x = img.unfold(2, self.patch_dim[1], self.patch_dim[2]).unfold(3, self.patch_dim[1], self.patch_dim[2])
x = x.contiguous().view(self.batch_size, channels, self.n_patches, self.patch_dim[1], self.patch_dim[2])
patches = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 4, 1)
x = patches.contiguous().view(self.batch_size, self.n_patches, self.embedding_dim)
x = self.projection(x)
cls_tokens = self.cls_token.repeat(self.batch_size, 1, 1)
x = torch.cat([cls_tokens, x], dim=1)
x = x + self.pos_embedding[:, :(self.n_patches+1)]
x = self.transformer(x)
x = x[:,0]
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.classification_head(x)
return x
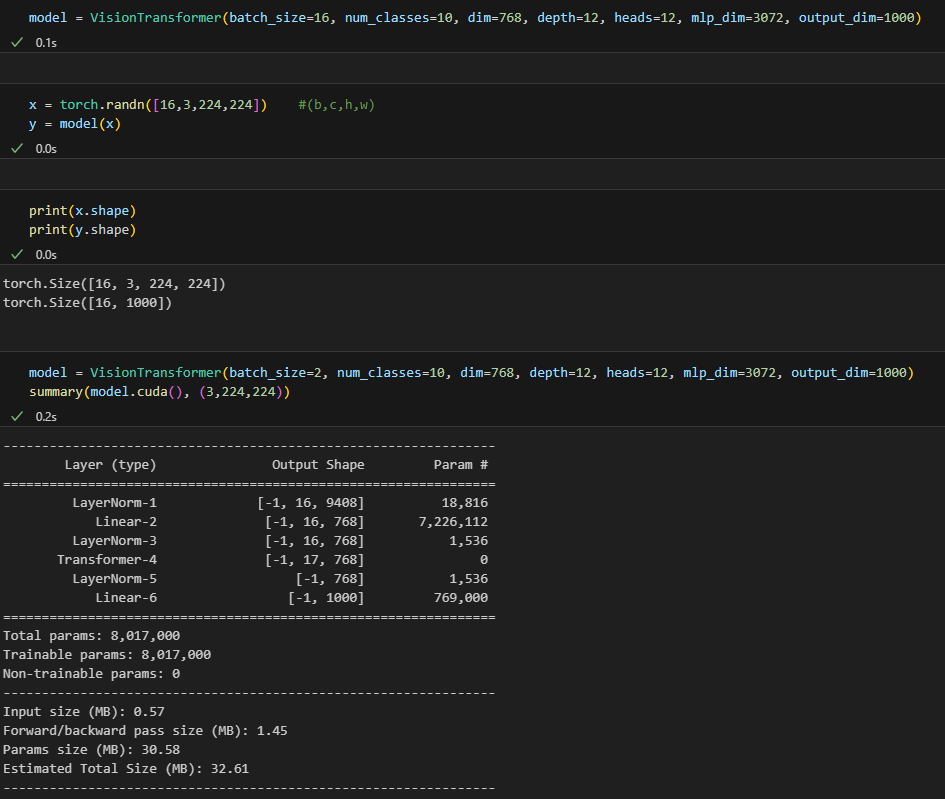
forward 과정과 torchsummary로 돌렸을때 문제없이 돌아가는걸 볼 수 있고 이후에 데이터셋까지 넣어 학습하는 예제까지 포스팅해보겠다.



